Our innovative services help us develop residential and commercial properties which are sustainable and stand the test of time. A few of these include Phytorid system, Organic Waste Converter, Rainwater Harvesting, HVAC system, MBBR and more. Each service serves a different purpose and benefits every project in several ways. Let's look at a few of our services, their meaning and advantages.
NEERI is a government research institute under the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research. It is one of the most reputed laboratories for environmental research and consultancy. The national environmental policy recommends using constructed wetland systems for efficient sewage treatment.
PHYTORID is a Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetland system (SSFCW) developed by the National Environmental Engineering Research Institute (NEERI).
The selection of technology for sewage treatment is based on varied parameters. This includes finding a plant which can work without electricity, requires minimum maintenance and is self-sustainable. National Environmental Engineering Research Institute (NEERI), Nagpur has developed a novel technology based on the natural method of treatment for sewage using constructed wetlands. The technology is named as PHYTORID and is patented nationally and internationally.
Use of plant species with their root system and the natural attenuation processes can be combined to get the Phytorid Technology. It is a technological solution, which can be implemented in cities and rural areas for the treatment of wastewater. The system is based on the use of specific plants typically found in natural reed with filtration and treatment capability. This system can be used for secondary and tertiary treatment of municipal wastewater, sludge management, treatment of industrial or agricultural effluent and more.
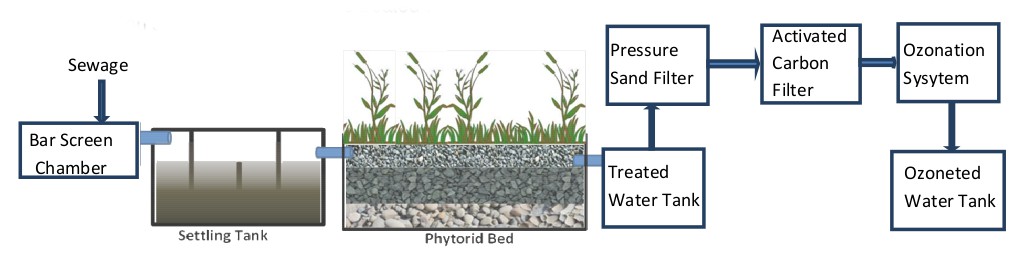
This system includes a bar screen chamber, settling tank, Phytorid bed, pressure sand filter, activated carbon filter & Ozonation system for disinfection and treated water tank. First, the wastewater from the screening chamber flows into the primary settling chamber thanks to gravity. Then, solids are separated and digested in an anaerobic manner. The next bed is called the Phytorid bed and is the heart of the system. Wastewater from the primary settling chamber flows into Phytorid bed by gravity. This bed is provided with a gradation of gravels/stone aggregate and hydrophytes types of plants. Next, the bed is divided into a compartment with baffles to ensure the flow of wastewater is in a sinusoidal manner.
This unique design provides both the anaerobic and aerobic zones in the same Phytorid bed. Aerobic zone is near roots of the plants, as plants transport oxygen from air to the roots and intern into the water for biochemical oxidation. A specially designed culture media helps in carrying biochemical oxidation in Phytorid bed. The flow of sewage is 6 inches below the gravel top layer, and therefore no sewage is exposed. This helps avoid mosquito problems. Plants also absorb nitrates and phosphates from the wastewater for further treatment. Due to several passages through gravel beds with both aerobic and anaerobic zones, faecal coliform is reduced by more than 99%. An ozonation treatment is added for disinfection. Treated water flows into a final storage tank by gravity, and the water quality meets the norms for reuse for irrigation.
The main objective of this project is to provide a simple and eco-friendly, maintenance-free and cost-effective technology, which can treat sewage water to reuse for purposes like gardening.
PHYTORID is a scientifically developed treatment method for wastewater. This treatment combines physical, biological and chemical processes. Also, this treatment works on gravity, does not need electric power and is cost-effective.
The proposed Phytorid system consists of a basin or a channel with a barrier to prevent seepage, but the beds contain a suitable depth of porous media. A primary treatment facility would also be constructed for effective removal of solids and thus reducing the marginal BOD.
The porous media also supports the root structure of emergent vegetation. The design of the Phytorid system assumes that the water level in the cells will remain below the top of the filter media.
The vegetation to be used for the said Phytorid system is important. Various species of aquatic plants have been used to attain maximum efficiency in the treatment of domestic wastes. These include species like Phragmites australis, Phalaris arundinacea, Glyceria maxima, Typha spp., Scirpus spp., other common grasses, etc.
This technology is a natural system; as a result operation is mostly passive and requires little operator intervention. Requirement for area can change on various factors such as load (kg BOD/day), ambient temperature, topography of the region, flow characteristics, etc. Maintaining uniform flow across the Phytorid system through inlet and outlet adjustment is extremely important to achieve the expected treatment performance. Sampling of inlet and outlet will be carried out for a period of 3 months every month and thereafter quarterly after stabilization of the treatment systems for first one year.
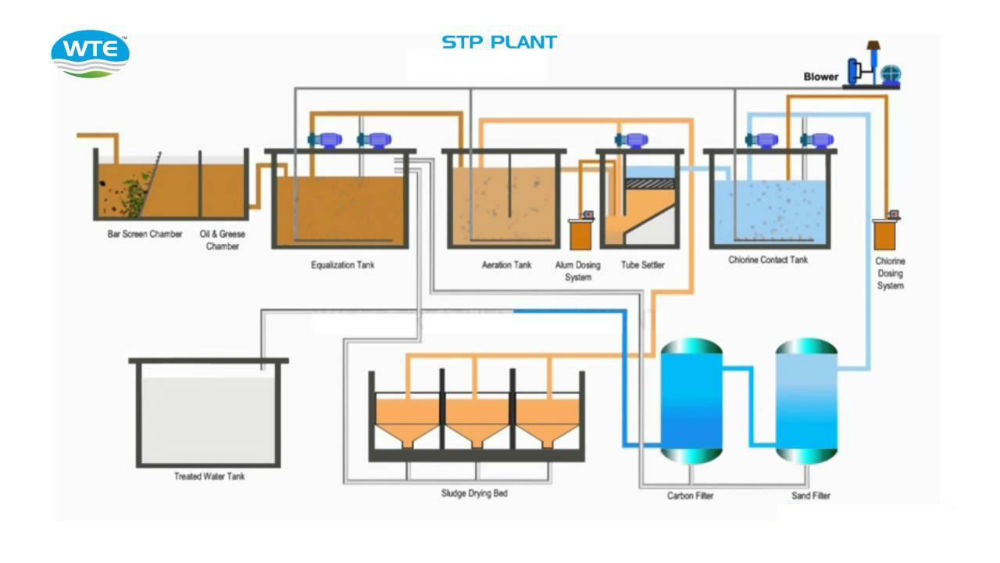
MBBR is a biofilm process. This technology is similar to Activated Sludge Process (ASP) except, here, the media suspended in the reactor provides microbes with additional surfaces to grow. This maximizes the growth of microbes in a given volume of aeration tank as compared to the conventional aeration.
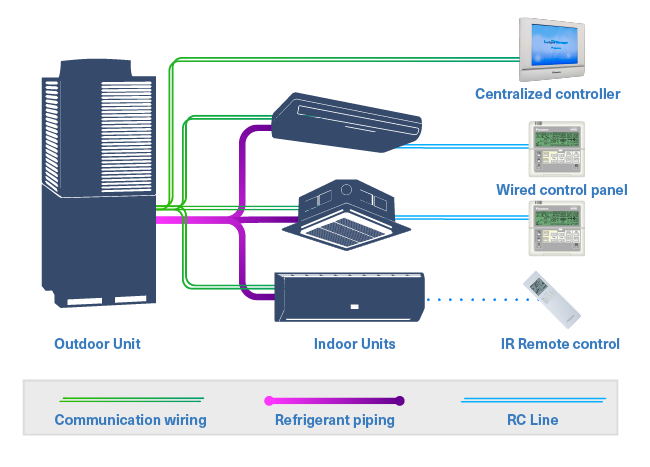
Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) systems are used as an enhanced version of multi-split systems, featuring simultaneous heating, cooling, and heat-recovery capabilities.
These systems are 20% to 30% more efficient than conventional HVAC systems. This is because of their partial load operation, speed modulation, zoning capabilities, and heat-recovery technology. Let's look at the benefits of using this system while developing residential and commercial properties in Pune, Mumbai, and elsewhere.
Composting is used to treat solid waste so that microorganisms break down the organic material, helping with the natural process of decay. This process requires organic waste such as leaves, grass, fruit and vegetable scraps, soil (which contains microorganisms), water, and oxygen. The organisms present in the soil eat the organic waste, breaking it down into its simplest components. The finished compost also called humus, is rich with fiber and inorganic nutrients such as phosphorus, potassium, and nitrogen. Owing to its rich organic nutrients, it makes it a natural fertilizer that is beneficial to the environment. Let's look at why Organic Waste Composter is necessary.
On average, food and garden waste make up over 1/3 of household waste. Buying food that goes to waste and disposing it off is expensive. By preventing food waste and composting, you can save money.
By composting at home, you reduce the need to collect, process, treat and dispose of biodegradable materials. This eventually saves landfill space and the fuel needed to move things around.
Compost can be beneficial – especially if you have made it at home. As it is full of nutrients and life, it improves the soil's fertility, texture, structure, moisture & nutrient-holding capacity. A healthy soil helps grow healthy, disease-resistant plants.
Peat moss from Ireland's bogs and peatlands has been used for years as a soil improver and potting mixes. Peatlands are home to species of flora and fauna. By composting at home, you won't have to purchase peat moss. This will, in turn, help protect the biodiversity of peatlands.
Today, there is still a lot of food and garden materials that end up in the landfill. They rot underground and produce foul liquids, odours, and methane, a greenhouse gas which is 21 times more potent than Carbon Dioxide. To avoid this and protect our environment, composting is the way everyone should choose and manage biodegradable materials.
Owing to the varied benefits of this process, we include Organic Waste Composter in our residential properties in Pune, Mumbai and other cities.
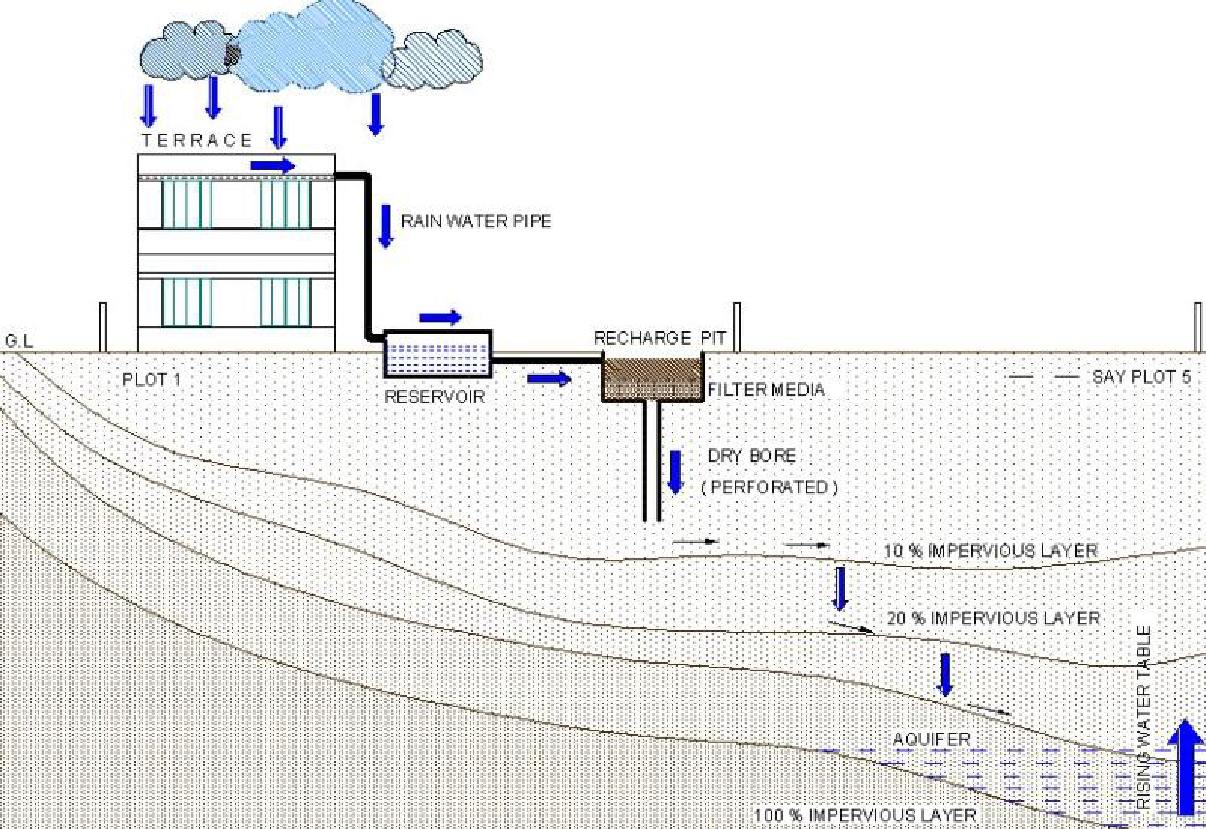
Rainwater harvesting consists of intercepting rainfall where it occurs and saving the water in various storage structures. These structures can be natural or humanmade, percolating it in the ground to raise water table levels. This helps prevent loss of water through evaporation and makes it easier to use it locally. There are varied benefits of collecting rainwater in advance and then using it for different purposes. Let's look at a few of them.